What Is Tracking ?
Tracking refers to the location, status, and activity of assets are monitored in real-time using technology.
Tracking in telematics is a powerful tool that allows you to gain complete visibility into your assets, leading to better decision-making, improved efficiency, and cost savings.
This is what Tracking entails in telematics;
Data Collection: Telematics devices installed on assets (vehicles, equipment, etc.) gather data using various methods;
- GPS: Tracks the precise location of the asset.
- Sensors: Monitor things like engine performance, fuel levels, temperature, or door open/closed status (depending on the application).
Transmission of Data: The collected data is sent wirelessly, typically through cellular networks, to a central server.
Data Analysis: Software on the server processes the data, transforming it into useful insights and reports.
What you can track with telematics
Location
See where your asset is on a map in real-time, perfect for fleet management or tracking deliveries.
Movement
Monitor historical movement patterns to understand how your assets are being used
Status
Get alerts for things like engine trouble, unauthorized movement, or harsh driving behaviors.
Performance
Analyze data like fuel consumption, engine diagnostics, or machine operation to identify potential issues and optimize performance
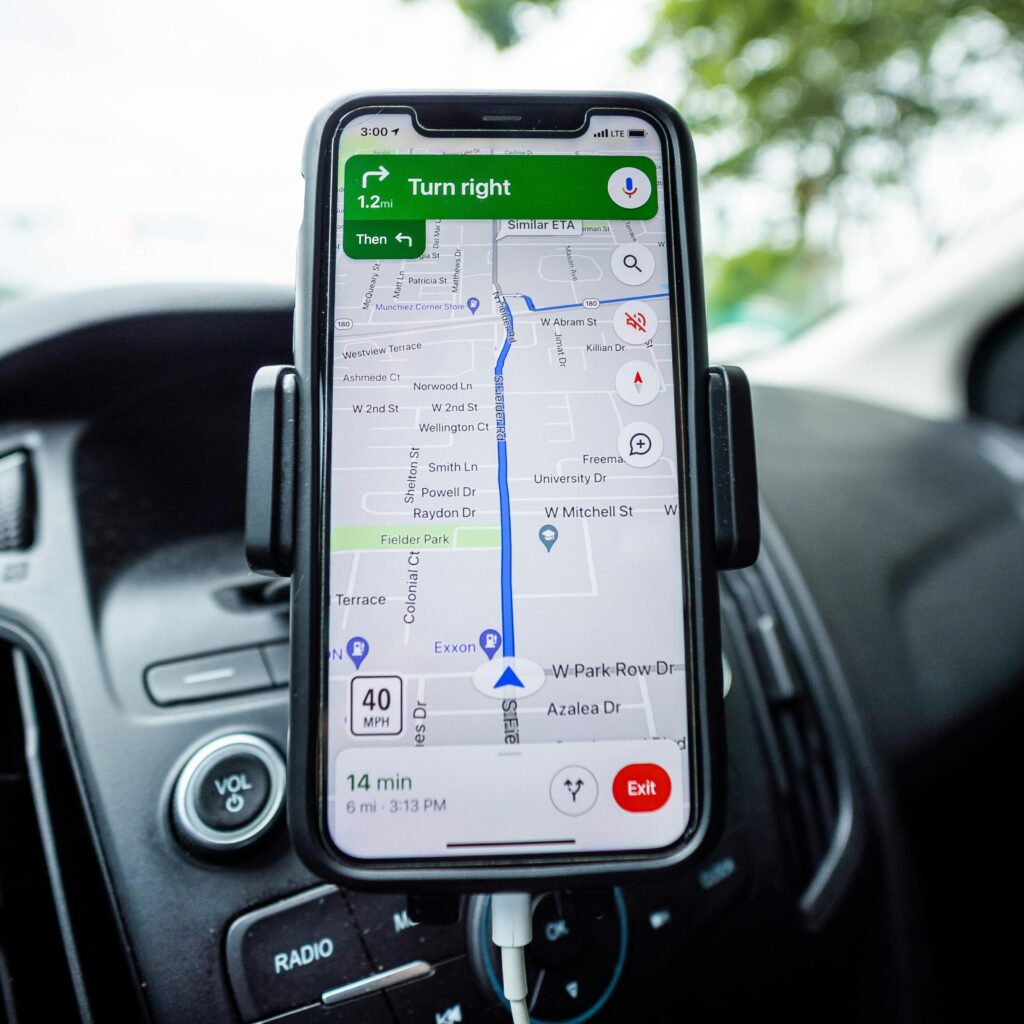
Real Time Tracking
Real-time tracking This is a core function of telematics which involves using GPS technology and other sensors to determine the exact location and status of an asset (usually a vehicle) at any given moment. This data is transmitted to a central system where it can be accessed and analyzed.
Benefits of real-time tracking It is designed for higher resource planning offers, advanced scheduling technology that optimizes fleet management through route efficiency (with the same base set of routing functions from Uber’s first mention due later today), fuel savings, and other factors.
Behavior Monitoring (Hazard Alerting) Standardized driver safety is enforced by behavior monitoring and hazard alerts. How you can prevent theft and loss through asset tracking, this leads to faster turn-around times and cost-reduction, thus improving operational efficiency. In the end, real-time tracking also assists with customer satisfaction via precise ETAs and service.
Applications of Real-Time Tracking
- Logistics and transportation: Track shipments, vehicles, and drivers for improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Asset management: Monitor the location and condition of valuable assets to prevent theft and loss.
- Personal safety: Track individuals, especially children, the elderly, otherwise those with special needs, for peace of mind.
- Field service: Monitor the location and progress of field service technicians to optimize service delivery.
- Environmental monitoring: Track wildlife, pollution levels, or natural disasters for environmental protection.
Challenges and Considerations
- Data privacy: Ensure that data is collected and stored securely and in compliance with relevant regulations.
- Network reliability: A stable and reliable communication network is essential for accurate tracking.
- Cost: The cost of implementing a real-time tracking system can vary depending on the scale and complexity of the application.