eSIM
What Is Asset Monitoring ?- Benefits and Managements
Asset monitoring is the broader concept that encompasses tracking within telematics. It refers to the process of overseeing and managing the performance, health, and status of various assets belonging to a company or individual.

Some valuable assets can be
- Vehicles
- Equipment
- Machinery
- Inventory
- Containers
- Packages
- High-Value goods
Benefits of Asset Monitoring
- Extended Asset Life: By identifying potential problems early on, you can prevent breakdowns and extend the lifespan of your assets.
- Improved Efficiency: Knowing the status and location of your assets allows for better resource allocation and streamlined operations.
- Reduced Costs: Preventive maintenance and optimized usage can save money on repairs, replacements, and downtime.
- Enhanced Security: Tracking assets helps deter theft and allows for faster recovery in case of loss.
- Compliance: Asset monitoring can help ensure compliance with regulations related to safety standards, environmental impact, or data security (depending on the asset type).
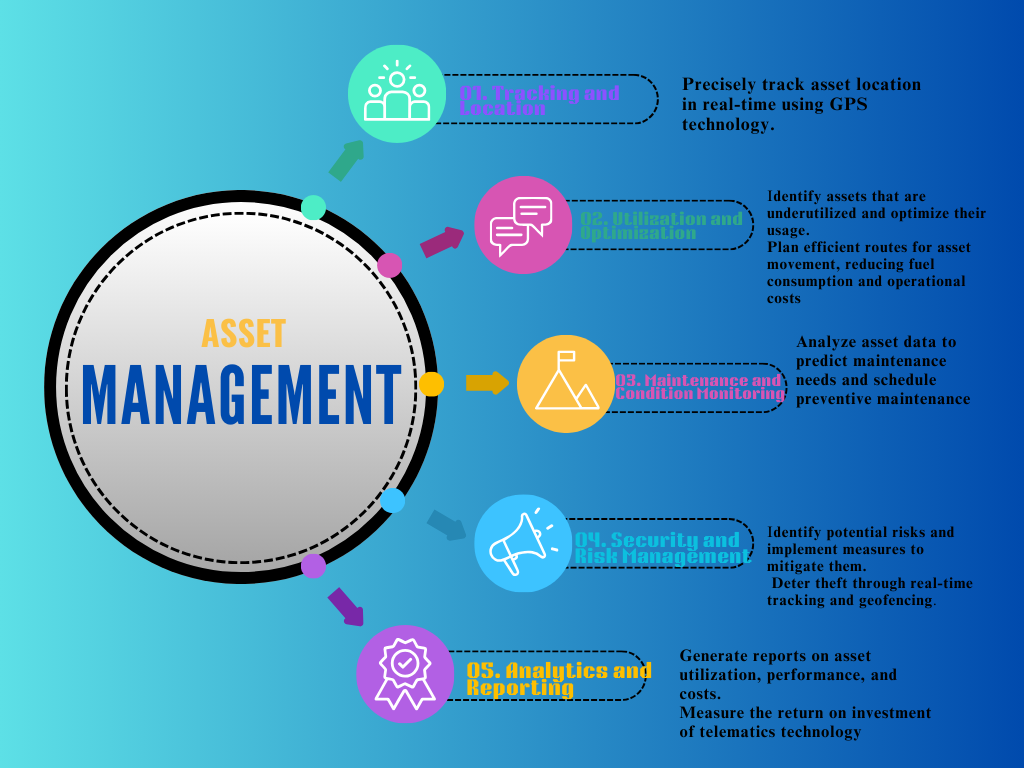
Asset Management
- Asset Tracking and Location:
- Real-time monitoring: Precisely track asset location in real-time using GPS technology.
- Geofencing: Set virtual boundaries to monitor asset movement and trigger alerts for unauthorized entry or exit.
- Asset recovery: Quickly locate and recover stolen or misplaced assets.
- Asset Utilization and Optimization:
- Idle time monitoring: Identify assets that are underutilized and optimize their usage.
- Route optimization: Plan efficient routes for asset movement, reducing fuel consumption and operational costs.
- Asset allocation: Distribute assets based on real-time demand and availability.
- Asset Maintenance and Condition Monitoring:
- Predictive maintenance: Analyze asset data to predict maintenance needs and schedule preventive maintenance.
- Condition monitoring: Track asset health parameters like engine temperature, fuel consumption, and tire pressure.
- Asset lifespan extension: Prolong asset life through timely maintenance and repairs.
- Asset Security and Risk Management:
- Theft prevention: Theft prevention deter theft through real-time tracking and geofencing.
- Unauthorized access alerts: Receive notifications for unauthorized asset access or tampering.
- Risk assessment: Risk assessment identify potential risks and implement measures to mitigate them.
- Data Analytics and Reporting:
- Performance analysis: Performance analysis generate reports on asset utilization, performance, and costs.
- Data-driven decision making: Use data insights to optimize asset management strategies.
- ROI analysis: ROI analysis measure the return on investment of telematics technology.
Asset Management in Telematics
Purpose if Asset Monitoring
Asset monitoring is a vital business practice that involves tracking and managing physical assets to prevent loss, theft, and unauthorized use. By using technologies like GPS, RFID, and sensors, businesses can gain real-time visibility into the location, condition, and usage of their assets. This information helps to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Real-time visibility is a key benefit of asset monitoring. By knowing the location of assets in real-time, businesses can respond quickly to emergencies, optimize delivery routes, and prevent unauthorized access. This level of visibility also enables companies to identify underutilized or overutilized assets, leading to more efficient resource allocation.
Predictive maintenance is another important application of asset monitoring. By collecting data on asset usage, condition, and maintenance history, businesses can use analytics to predict potential failures before they occur. This proactive approach can help prevent costly downtime, extend the lifespan of assets, and reduce overall maintenance costs.
Data-driven decision-making is essential for businesses to remain competitive. Asset monitoring provides a wealth of data that can be used to inform strategic decisions. For example, businesses can analyze asset usage patterns to identify opportunities for process improvement or new product development.

