Geofencing in telematics enhances fleet management by providing precise location-based insights, improving operational efficiency, ensuring regulatory compliance, and enhancing security measures to protect assets and personnel. Its integration with advanced telematics systems continues to redefine how businesses optimize logistics and streamline operations in a competitive marketplace.

Applications Of Geofencing
-
- Retail and Marketing
-
- Targeted advertising and promotions based on customer location.
-
- Enhancing customer engagement through personalized offers.
-
- Retail and Marketing
-
- Logistics and Fleet Management
-
- Tracking shipments and vehicles within defined areas.
-
- Optimizing delivery routes and schedules.
-
- Logistics and Fleet Management
-
- Security and Surveillance
-
- Monitoring restricted areas and triggering alerts for unauthorized entry.
-
- Enhancing perimeter security for buildings and facilities.
-
- Security and Surveillance
-
- Smart Cities
-
- Managing traffic flow and congestion through dynamic routing.
-
- Providing location-based services to residents and visitors
-
- Smart Cities
How It Works
Geofencing works by using geographic boundaries (virtual perimeters) defined by GPS coordinates or other location-based technologies to trigger actions when a device, typically a smartphone or a GPS-enabled device, enters or exits the designated area.
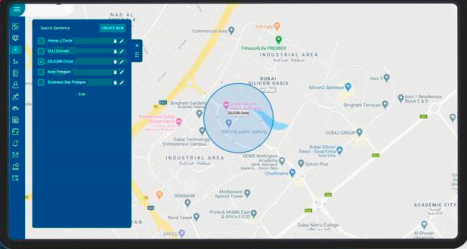
A representation of a geofencing.
Geofencing Accuracy In Telematics
Factors That Can Influence The Accuracy Of Geofencing :
There are several factors that influence the geofencing accuracy in telematics;
- GPS signal strength: A strong GPS signal is essential for precise location data. Obstacles like buildings or dense foliage can interfere with the signal.
- Device quality: The quality of the GPS device used in the telematics system directly impacts accuracy. Higher-end devices with advanced GPS capabilities will generally provide more accurate results.
- Geofence size and shape: Larger geofences are less sensitive to minor location variations than smaller ones. Irregularly shaped geofences might also impact accuracy.
- Real-world conditions: Factors like traffic congestion, tunnels, or underground parking can affect GPS accuracy and, consequently, geofencing.
Improving Geofencing Accuracy
To enhance improving geofencing accuracy, consider the following;
- Redundant positioning systems: Combining GPS with other positioning technologies like cellular triangulation or Wi-Fi can improve accuracy in challenging environments.
- Geofence optimization: Regularly review and adjust geofence boundaries to ensure they accurately reflect the desired areas.
- Data filtering: Implementing data filtering techniques can help to remove erroneous location data points.
- Advanced algorithms: Using sophisticated algorithms to process location data can improve geofencing precision