eSIM
What Is Fleet ? Fleet Maintenance and Driver Safety
A fleet is a group of Vehicles, Ships or Aircraft that are owned, operated, or managed by a single entity, such as a company, government, or organization. Fleets are often used for transportation, logistics, or other business purposes.
A well-managed fleet is essential for businesses that rely on vehicles to transport goods or services. By implementing effective fleet management strategies, you can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance overall operations. Fleet management is a critical aspect of many businesses, from transportation companies to delivery services and construction firms. By effectively managing their fleets, organizations can improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.

Types of Fleet
There are several types of fleet, classified on the vehicle type, purpose or industry being used, here are some types of fleets;
- Passenger Fleets: Passenger fleets are vehicles used for the transportation of people, for instance;
- Taxi fleet
- Ride-hailing fleets (uber, lyft )
- Shuttle fleet (airport, hotel)
- Bus fleet
- Commercial fleets: Commercial fleets are vehicles used for business purposes, for instance;
- Delivery fleet (parcel, food, package)
- Sales fleet (company cars, sales van )
- Specialty fleet: Specialty fleets are vehicles used for a specific purposes, for instance;
- Racing
- Recreational fleet (motorhomes)
- Historic fleets (vintage cars, antique trucks)
- Emergency fleets: Emergency fleets are vehicles used for emergency response, for instance;
- Police fleet
- Fire fleet ( fire trucks, ambulances)
- Industrial fleets: Industrial fleets are vehicles used in various industrial settings, for instance;
- Construction fleet (trucks, cranes, excavators)
- Mining fleet (heavy equipment, haul trucks)
- Agricultural fleet (tractors, combines, farm trucks)
Fleet Maintenance
Fleet maintenance: Fleet maintenance is the systematic process of ensuring that your company’s vehicles are in optimal condition for safe and efficient operation. It’s more than just routine checks; it’s a strategic approach to maximizing vehicle lifespan, minimizing downtime, and controlling costs.
Importance of Fleet Maintenance
- Safety: Well-maintained vehicles reduce the risk of accidents, protecting drivers and other road users.
- Reliability: Regular servicing prevents breakdowns, ensuring vehicles are always ready for duty.
- Asset Value: Proper care increases the resale value of your fleet.
- Cost-efficiency: Preventive maintenance catches issues early, preventing costly repairs and maximizing fuel efficiency.
Fleet Maintenance Best Practices
Some of the best practices you need to apply in fleet maintenance is as follows;
- Monitor Key Performance Indicators: Track maintenance costs, downtime, fuel consumption, and other metrics to measure performance.
- Choose Quality Parts and Service Providers: Invest in reliable components and skilled technicians.
- Train Your Drivers: Educate drivers about the importance of vehicle care and reporting issues promptly.
- Utilize Fleet Management Software: Streamline maintenance scheduling, record keeping, and reporting.
- Develop a Comprehensive Maintenance Plan: Tailor a plan to your specific fleet and vehicle types.
Fleet Management and Optimization
Fleet management and optimization go hand-in-hand. This is a broad process of overseeing and controlling a group of commercial vehicles, while optimization focuses on using data and technology to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and achieve specific goals within that fleet management system.

By staying ahead of these trends and utilizing technology effectively, businesses can leverage fleet management also optimization to gain a significant competitive advantage.
Fleet Management (The Foundation)
- Core Activities: Fleet management covers the entire lifecycle of vehicles, including acquisition (purchase/lease), maintenance scheduling, driver management, fuel management, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Data Collection: Telematics systems and various tracking tools gather data on vehicle location, performance, driver behavior, and fuel consumption.
Optimization(Taking it to the Next Level)
- Leveraging Data: Optimization utilizes the data collected through fleet management to make informed decisions and identify areas for improvement.
- Technology Integration: Fleet management software integrates with telematics data to provide insights and automate tasks. For example, software can;
- Optimize Routes: Plan efficient routes that minimize travel time, distance, and fuel consumption.
- Predict Maintenance Needs: Analyze data to predict potential equipment failures and schedule preventive maintenance, preventing costly breakdowns.
- Monitor Driver Behavior: Track driver performance to identify areas for improvement like speeding or harsh braking, promoting safer driving habits.
- Reduce Fuel Costs: Track fuel efficiency and suggest strategies like route adjustments or fuel-efficient driving techniques.
Benefits of Combined Approach
- Reduced Operational Costs: Optimizing routes and driver behavior leads to significant savings on fuel, maintenance, and vehicle wear-and-tear
- Improved Efficiency: Data-driven decision-making and automation streamline processes, leading to faster completion times for deliveries or services.
- Enhanced Safety: Monitoring driver behavior and proactive maintenance reduce accidents also ensure drivers are well-rested and following safety protocols.
- Increased Productivity: By optimizing tasks and reducing downtime, fleets can achieve more with the same resources.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Insights from data analysis help fleet managers make informed strategic decisions about vehicle acquisition, resource allocation, and overall fleet operations.
Driver Safety
Driver safety is paramount for everyone on the road. It involves a combination of responsible behavior, vehicle maintenance, and road awareness. There is practice of be taken precautionary to prevent accidents and injuries while driving.
Every time you get behind the wheel, you have a responsibility to ensure your own safety and the safety of others on the road. Driver safety is more than just following the rules; it’s about adopting a cautious and responsible mindset.
Some factors for driver safety includes
- Driver Focus and Attention
- Minimize distractions: Avoid using phones, eating, or engaging in other activities while driving.
- Maintain situational awareness: Be constantly aware of your surroundings, including other vehicles, pedestrians, and road conditions.
- Vehicle Condition
- Regular maintenance: Ensure your vehicle is in good working order, including brakes, tires, lights, and engine.
- Safety features: Utilize advanced safety technologies such as anti-lock brakes, electronic stability control, and airbags.
- Road Conditions and Environment
- Weather awareness: Adjust driving speed and techniques based on weather conditions (rain, snow, fog, etc.).
- Road hazards: Be cautious of potholes, construction zones, and wildlife.
- Driving Behavior
- Speed control: Adhere to posted speed limits and adjust speed based on road conditions.
- Defensive driving: Anticipate the actions of other drivers and maintain a safe following distance.
- Driver Fitness
- Impairment avoidance: Refrain from driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Sufficient rest: Ensure you are well-rested before driving long distances.
Geofencing: Its Uses, How It Works & Its Accuracy In Telematics.
Geofencing in telematics enhances fleet management by providing precise location-based insights, improving operational efficiency, ensuring regulatory compliance, and enhancing security measures to protect assets and personnel. Its integration with advanced telematics systems continues to redefine how businesses optimize logistics and streamline operations in a competitive marketplace.

Applications Of Geofencing
-
- Retail and Marketing
-
- Targeted advertising and promotions based on customer location.
-
- Enhancing customer engagement through personalized offers.
-
- Retail and Marketing
-
- Logistics and Fleet Management
-
- Tracking shipments and vehicles within defined areas.
-
- Optimizing delivery routes and schedules.
-
- Logistics and Fleet Management
-
- Security and Surveillance
-
- Monitoring restricted areas and triggering alerts for unauthorized entry.
-
- Enhancing perimeter security for buildings and facilities.
-
- Security and Surveillance
-
- Smart Cities
-
- Managing traffic flow and congestion through dynamic routing.
-
- Providing location-based services to residents and visitors
-
- Smart Cities
How It Works
Geofencing works by using geographic boundaries (virtual perimeters) defined by GPS coordinates or other location-based technologies to trigger actions when a device, typically a smartphone or a GPS-enabled device, enters or exits the designated area.
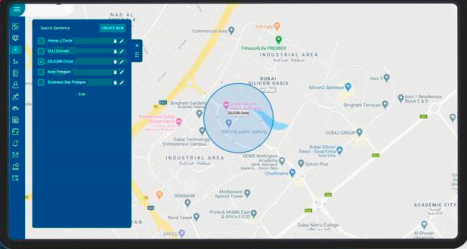
A representation of a geofencing.
Geofencing Accuracy In Telematics
Factors That Can Influence The Accuracy Of Geofencing :
There are several factors that influence the geofencing accuracy in telematics;
- GPS signal strength: A strong GPS signal is essential for precise location data. Obstacles like buildings or dense foliage can interfere with the signal.
- Device quality: The quality of the GPS device used in the telematics system directly impacts accuracy. Higher-end devices with advanced GPS capabilities will generally provide more accurate results.
- Geofence size and shape: Larger geofences are less sensitive to minor location variations than smaller ones. Irregularly shaped geofences might also impact accuracy.
- Real-world conditions: Factors like traffic congestion, tunnels, or underground parking can affect GPS accuracy and, consequently, geofencing.
Improving Geofencing Accuracy
To enhance improving geofencing accuracy, consider the following;
- Redundant positioning systems: Combining GPS with other positioning technologies like cellular triangulation or Wi-Fi can improve accuracy in challenging environments.
- Geofence optimization: Regularly review and adjust geofence boundaries to ensure they accurately reflect the desired areas.
- Data filtering: Implementing data filtering techniques can help to remove erroneous location data points.
- Advanced algorithms: Using sophisticated algorithms to process location data can improve geofencing precision
What Is Asset Monitoring ?- Benefits and Managements
Asset monitoring is the broader concept that encompasses tracking within telematics. It refers to the process of overseeing and managing the performance, health, and status of various assets belonging to a company or individual.

Some valuable assets can be
- Vehicles
- Equipment
- Machinery
- Inventory
- Containers
- Packages
- High-Value goods
Benefits of Asset Monitoring
- Extended Asset Life: By identifying potential problems early on, you can prevent breakdowns and extend the lifespan of your assets.
- Improved Efficiency: Knowing the status and location of your assets allows for better resource allocation and streamlined operations.
- Reduced Costs: Preventive maintenance and optimized usage can save money on repairs, replacements, and downtime.
- Enhanced Security: Tracking assets helps deter theft and allows for faster recovery in case of loss.
- Compliance: Asset monitoring can help ensure compliance with regulations related to safety standards, environmental impact, or data security (depending on the asset type).
Asset Management
- Asset Tracking and Location:
- Real-time monitoring: Precisely track asset location in real-time using GPS technology.
- Geofencing: Set virtual boundaries to monitor asset movement and trigger alerts for unauthorized entry or exit.
- Asset recovery: Quickly locate and recover stolen or misplaced assets.
- Asset Utilization and Optimization:
- Idle time monitoring: Identify assets that are underutilized and optimize their usage.
- Route optimization: Plan efficient routes for asset movement, reducing fuel consumption and operational costs.
- Asset allocation: Distribute assets based on real-time demand and availability.
- Asset Maintenance and Condition Monitoring:
- Predictive maintenance: Analyze asset data to predict maintenance needs and schedule preventive maintenance.
- Condition monitoring: Track asset health parameters like engine temperature, fuel consumption, and tire pressure.
- Asset lifespan extension: Prolong asset life through timely maintenance and repairs.
- Asset Security and Risk Management:
- Theft prevention: Theft prevention deter theft through real-time tracking and geofencing.
- Unauthorized access alerts: Receive notifications for unauthorized asset access or tampering.
- Risk assessment: Risk assessment identify potential risks and implement measures to mitigate them.
- Data Analytics and Reporting:
- Performance analysis: Performance analysis generate reports on asset utilization, performance, and costs.
- Data-driven decision making: Use data insights to optimize asset management strategies.
- ROI analysis: ROI analysis measure the return on investment of telematics technology.
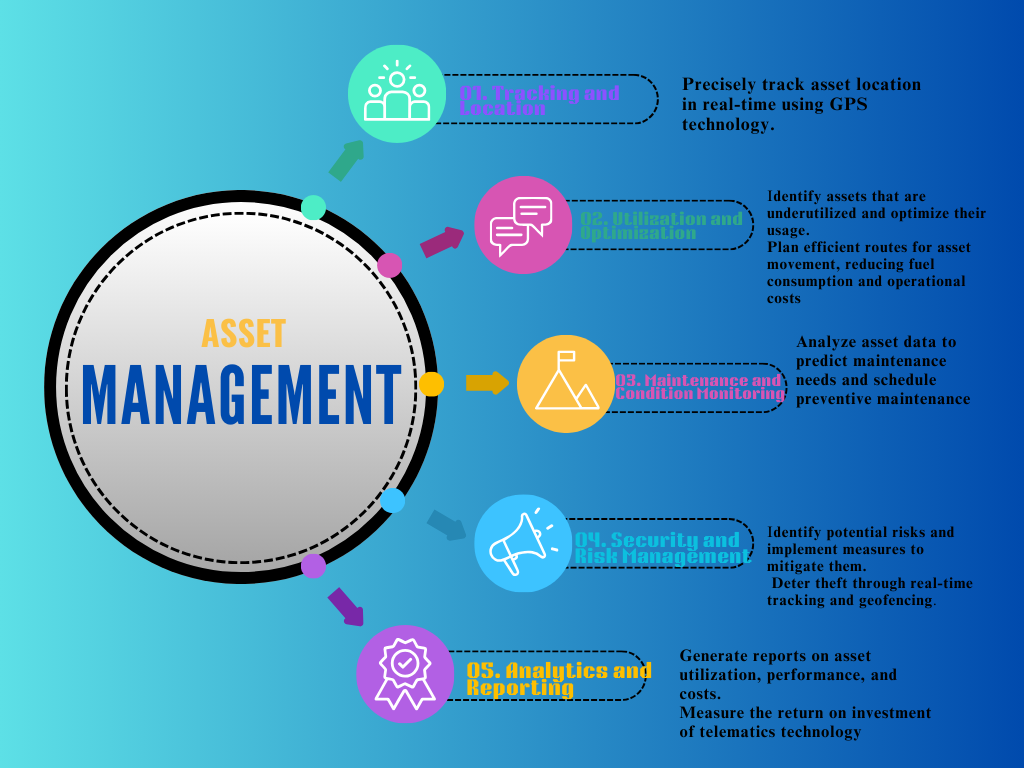
Asset Management in Telematics
Purpose if Asset Monitoring
Asset monitoring is a vital business practice that involves tracking and managing physical assets to prevent loss, theft, and unauthorized use. By using technologies like GPS, RFID, and sensors, businesses can gain real-time visibility into the location, condition, and usage of their assets. This information helps to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Real-time visibility is a key benefit of asset monitoring. By knowing the location of assets in real-time, businesses can respond quickly to emergencies, optimize delivery routes, and prevent unauthorized access. This level of visibility also enables companies to identify underutilized or overutilized assets, leading to more efficient resource allocation.
Predictive maintenance is another important application of asset monitoring. By collecting data on asset usage, condition, and maintenance history, businesses can use analytics to predict potential failures before they occur. This proactive approach can help prevent costly downtime, extend the lifespan of assets, and reduce overall maintenance costs.
Data-driven decision-making is essential for businesses to remain competitive. Asset monitoring provides a wealth of data that can be used to inform strategic decisions. For example, businesses can analyze asset usage patterns to identify opportunities for process improvement or new product development.
How To Track Your Devices: Real-Time Tracking
What Is Tracking ?
Tracking refers to the location, status, and activity of assets are monitored in real-time using technology.
Tracking in telematics is a powerful tool that allows you to gain complete visibility into your assets, leading to better decision-making, improved efficiency, and cost savings.
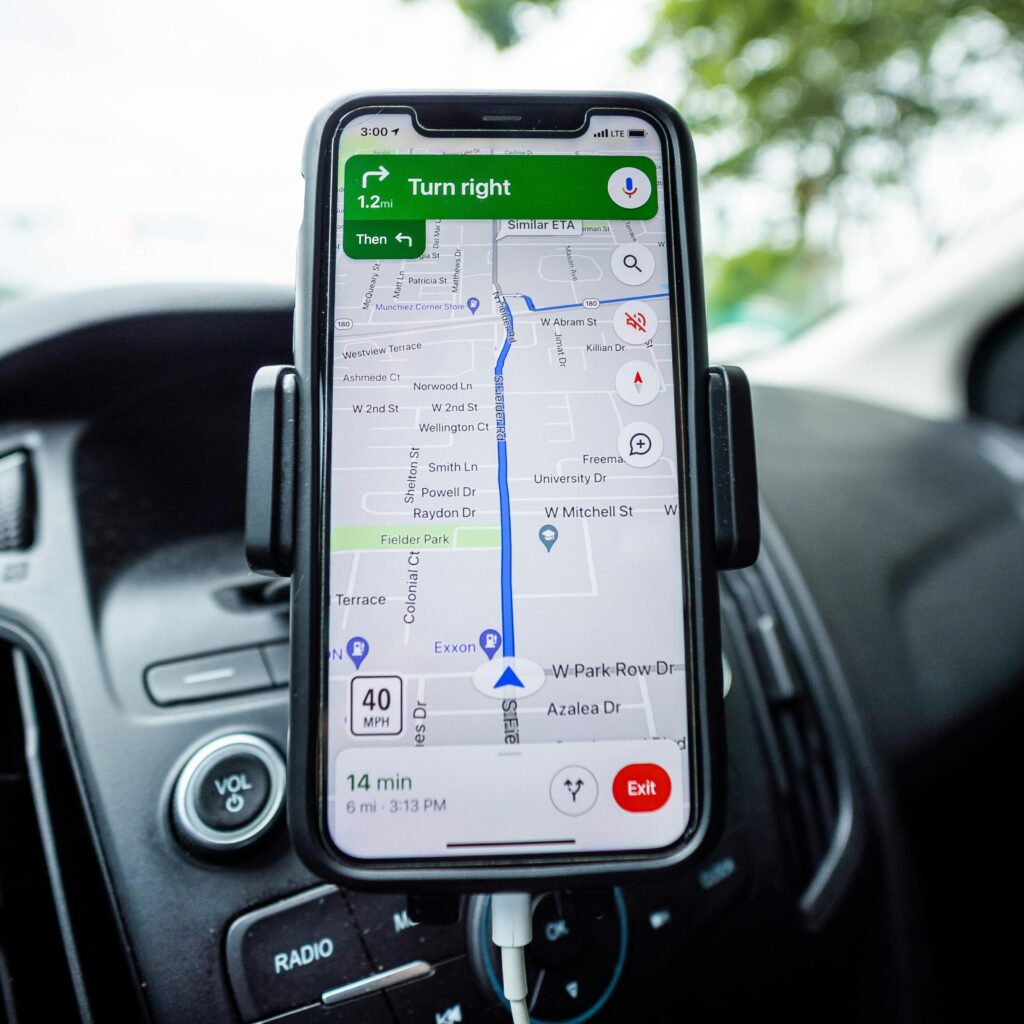
This is what Tracking entails in telematics;
Data Collection: Telematics devices installed on assets (vehicles, equipment, etc.) gather data using various methods;
- GPS: Tracks the precise location of the asset.
- Sensors: Monitor things like engine performance, fuel levels, temperature, or door open/closed status (depending on the application).
Transmission of Data: The collected data is sent wirelessly, typically through cellular networks, to a central server.
Data Analysis: Software on the server processes the data, transforming it into useful insights and reports.
What you can track with telematics
Location
See where your asset is on a map in real-time, perfect for fleet management or tracking deliveries.
Movement
Monitor historical movement patterns to understand how your assets are being used
Status
Get alerts for things like engine trouble, unauthorized movement, or harsh driving behaviors.
Performance
Analyze data like fuel consumption, engine diagnostics, or machine operation to identify potential issues and optimize performance
Real Time Tracking
Real-time tracking This is a core function of telematics which involves using GPS technology and other sensors to determine the exact location and status of an asset (usually a vehicle) at any given moment. This data is transmitted to a central system where it can be accessed and analyzed.
Benefits of real-time tracking It is designed for higher resource planning offers, advanced scheduling technology that optimizes fleet management through route efficiency (with the same base set of routing functions from Uber’s first mention due later today), fuel savings, and other factors.
Behavior Monitoring (Hazard Alerting) Standardized driver safety is enforced by behavior monitoring and hazard alerts. How you can prevent theft and loss through asset tracking, this leads to faster turn-around times and cost-reduction, thus improving operational efficiency. In the end, real-time tracking also assists with customer satisfaction via precise ETAs and service.
Applications of Real-Time Tracking
- Logistics and transportation: Track shipments, vehicles, and drivers for improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Asset management: Monitor the location and condition of valuable assets to prevent theft and loss.
- Personal safety: Track individuals, especially children, the elderly, otherwise those with special needs, for peace of mind.
- Field service: Monitor the location and progress of field service technicians to optimize service delivery.
- Environmental monitoring: Track wildlife, pollution levels, or natural disasters for environmental protection.
Challenges and Considerations
- Data privacy: Ensure that data is collected and stored securely and in compliance with relevant regulations.
- Network reliability: A stable and reliable communication network is essential for accurate tracking.
- Cost: The cost of implementing a real-time tracking system can vary depending on the scale and complexity of the application.
What’s Telematics?-Benefits and Business Operations In Fleets.
Imagine having a virtual assistant that tracks your important things no matter where they go. That’s telematics! It combines wireless communication (like cell phones) with data analysis to give you insights.